The European Union’s greenhouse gas emissions fell slightly in the second quarter of 2025, with Cyprus among the few countries achieving a combination of lower emissions and economic growth.
Specifically, Eurostat on Friday reported that emissions across the EU economy were estimated at 772 million tonnes of CO₂-equivalents in the second quarter of 2025.
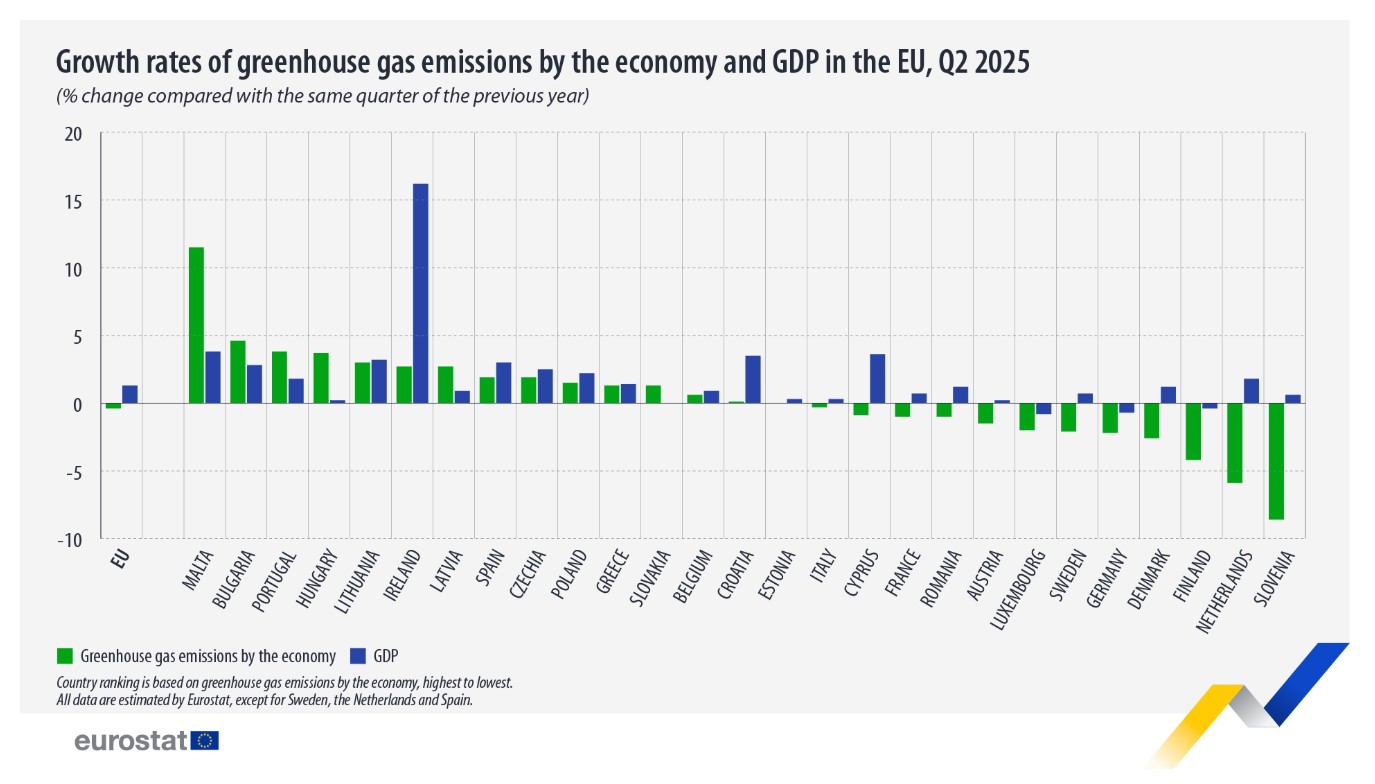
This represented a 0.4 per cent decrease compared with the same quarter of 2024, when emissions stood at 775 million tonnes.
Over the same period, the EU’s gross domestic product increased by 1.3 per cent, underscoring a continued decoupling trend between economic growth and emissions.
Eurostat said that the figures form part of its quarterly estimates on greenhouse gas emissions by economic activity, which complement socio-economic data such as GDP and employment.
It added that the new release highlights the main findings of its broader Statistics Explained article on quarterly greenhouse gas emissions.
The sectors showing the largest year-on-year decreases were electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply, which fell by 2.9 per cent.
Manufacturing posted a 0.4 per cent reduction. Transportation and storage also declined by 0.4 per cent.
Household emissions moved in the opposite direction, increasing by 1.0 per cent.
Across the EU, year-on-year emissions increased in 14 member states, decreased in 12 and remained unchanged in Estonia.
The largest reductions were recorded in Slovenia with a fall of 8.6 per cent, the Netherlands with 5.9 per cent, and Finland with 4.2 per cent.
Of the 12 countries that reduced emissions, three (Finland, Germany and Luxembourg) also experienced a decline in GDP.
The remaining nine, including Cyprus, saw emissions decrease while their economies continued to grow.
This places Cyprus among the member states achieving the dual objective of lowering emissions while supporting economic expansion, a trend increasingly prioritised in EU climate assessments.
It should be mentioned that the remaining member states who also grew their economies while reducing emissions were Austria, Denmark, France, Italy, the Netherlands, Romania, Slovenia and Sweden.






Click here to change your cookie preferences